基于 Etcd 实现的服务注册和发现的 grpclb 参见: grpclb
前提
gRPC 负载均衡是针对每次请求,而不是连接,这样可以保证服务端负载的均衡性。负载均衡器按照实现侧不同一般分为两种:
1. Proxy
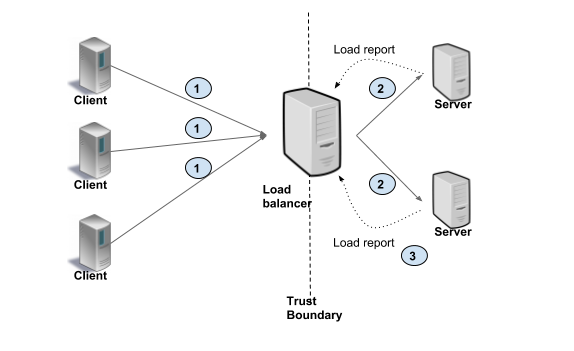
2. Client Side
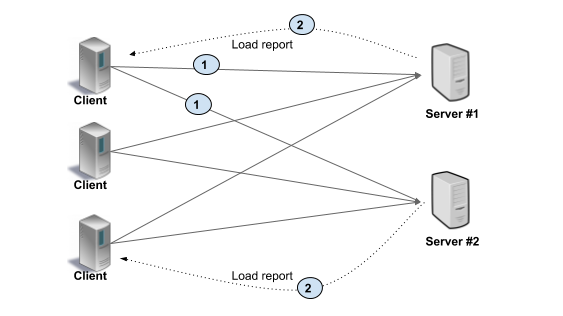
Thick Client
所有负载均衡算法实现都在客户端。
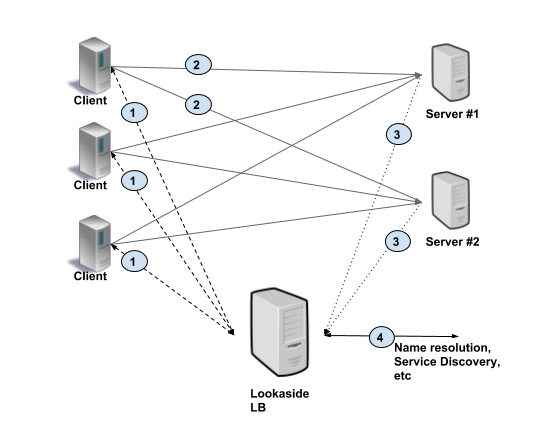
Lookaside Load Balancing
也称单臂路由。
Etcd Loadbanlacer 实现
gPRC 当前最新版本为 Release 1.14.0,由于 Etcd 不同版本的 Banlancer 实现方式不仅相同,可以参考:client-architecture/ Etcd v3.4.0 (TBD 2018-09)。组合条件有以下几类算法:
clientv3-grpc1.0
客户端同时保留与服务端 Nodes 多个连接,在出现错误时候,可以快速重试其他的连接
limit: 保持多个连接浪费资源;对于 Nodes 的健康状态或者集群 Membership 关系未知,在某个 Node 出现问题时可能不能正常工作。

clientv3-grpc1.7 (可选者方案)
与服务端中的某一个 Node 保持连接。当集群中有多个endpoints 时候,尝试连接到所有的 endpoints,一旦选中了一个连接(pinned address),关闭其他的连接,直至该连接被关闭。如果调用中间出现错误,则进入错误处理流程。





限制:使用 HTTP/2 keepalives 来保持心跳,可能会出现脑裂的情况。


- clientv3-grpc1.14 (v3.4.0 开发中)
gRPC 1.14 LD 分析

dnsResolver
注册 dnsResolver:
1 | func init() { |
Resolver 的 Builder 接口。Builder 会创建一个用于监视名称解析更新的 resolver 。
1 | // Builder creates a resolver that will be used to watch name resolution updates. |
Resover 的接口定义如下:
1 | // Resolver watches for the updates on the specified target. |
代码分析,首先 NewBuilder 作为一个工厂来创建一个 resolver.Builder,供 gRPC 程序来进行调用:
1 | // NewBuilder creates a dnsBuilder which is used to factory DNS resolvers. |
dnsResolver 结构定义如下:
1 | // dnsResolver watches for the name resolution update for a non-IP target. |
Build 创建并启动一个 DNS 解析器,用于监视目标的名称解析。
1 | // Build creates and starts a DNS resolver that watches the name resolution of the target. |
传入参数 cc resolver.ClientConn,ClientConn 包含 resolver 的回调,以通知 gRPC ClientConn 的任何更新。
1 | // ClientConn contains the callbacks for resolver to notify any updates |
watcher 函数的实现如下:
1 | func (d *dnsResolver) watcher() { |
通过 Close 函数的调用来达到停止 watcher 的效果:
1 | // Close closes the dnsResolver. |
RR Balancer

Banlancer Builder 接口定义如下:
1 | // Builder creates a balancer. |
Banlancer 接口定义如下:
1 | // Balancer takes input from gRPC, manages SubConns, and collects and aggregates |
banlancer/base 中实现了大多数 banlancer 功能,不同选择算法的实现,基于 base 实现 pickBuilder 与 picker 接口即可。
base.NewBalancerBuilder 函数定义如下:
1 | // Base 实现的函数 |
RR Banlancer 的实现基于 balancer/base 基础实现,核心功能主体在 balancer/base 中实现,而 RR Banlancer 基于 base.NewBalancerBuilder 实现了 balancer.Builder 接口,可以用于注册。
1 | // Name is the name of round_robin balancer. |
PickerBuilder 接口定义如下:
1 | // PickerBuilder creates balancer.Picker. |
RoundRobin Banlancer Builder 实现了 PickerBuilder 的接口:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11func (*rrPickerBuilder) Build(readySCs map[resolver.Address]balancer.SubConn) balancer.Picker {
grpclog.Infof("roundrobinPicker: newPicker called with readySCs: %v", readySCs)
// 将 map 接口转化成 slice[] 结构,并使用期构造 rrPicker 并返回
var scs []balancer.SubConn
for _, sc := range readySCs {
scs = append(scs, sc)
}
return &rrPicker{
subConns: scs,
}
}
banlancer.Picker 由 rrPicker 来实现:
1 | type rrPicker struct { |
Etcd 服务注册与发现
clientv3-grpc1.14: Official client implementation, with grpc-go v1.14.x, which is used in latest etcd v3.4.
etcdv3Client -> autoSync() -> Sync() -> c.SetEndpoints(eps…) -> gc.resolverGroup.SetEndpoints(eps) -> EveryResover -> ClientConn update
参考
- gRPC Load Balancing
- Load Balancing in gRPC
- gRPC服务发现&负载均衡
- go语言gRPC负载均衡库grpc-lb的使用
- bsm/grpclb External Load Balancing Service solution for gRPC written in Go
- Writing gRPC Interceptors in Go
- proposal/L9-go-resolver-balancer-API.md
- https://github.com/DavadDi/wonaming
- etcd学习笔记(etcdv3, gRPC服务发现和负载均衡)
- etcd v3 服务注册与发现 Go代码
- https://godoc.org/github.com/coreos/etcd/clientv3/namespace 自动使用前缀
- 使用gvm管理多版本golang gvm 管理多个 golang 环境,类似于 python virtural env 方式